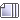
evo medicinskog opravdanja o ronijevom laktu...
Well as a concerned Coleman fan I did some googling to find out what indeed Bursitis is.
source:
http://orthopedics.about.com/cs/elbow/a/olecranonbursa.htmWhat is a bursa?
Every person has hundreds of bursa scattered throughout the body. The function of a bursa is to decrease friction between two surfaces that move in different directions.
The bursa can be thought of as a Ziplock bag with a small amount of oil and no air inside. Imagine rubbing this bag between your hands; movement of your hands would be smooth and effortless. That is what a bursa functions as--a smooth, slippery surface between two moving objects.
You tend to find a bursa at points where muscles and tendons glide over bones. Without the bursa between these surfaces, movements would be painful.
What is bursitis?
Bursitis is the inflammation of a bursa. Normally, the bursa provides a slippery surface that has almost no friction.
A problem arises when a bursa becomes inflamed. The bursa loses its gliding capabilities, and becomes more and more irritated when it is moved.
When the condition called bursitis occurs, the normally slippery bursa becomes swollen and inflamed. The added bulk of the swollen bursa causes more friction within an already confined space. Also, the smooth gliding bursa becomes gritty and rough. Movement of an inflamed bursa is painful and irritating.
What causes bursitis?
Bursitis usually results from a repetitive movement or due to prolonged and excessive pressure. Patients who rest on their elbows for long periods or those who bend their elbows frequently and repetitively (for example, a custodian using a vacuum for hours at a time) can develop elbow bursitis, also called olecranon bursitis. Similarly in other parts of the body, repetitive use or frequent pressure can irritate a bursa and cause inflammation.
Another cause of bursitis is a traumatic injury. Following trauma, such as a car accident or fall, a patient may develop bursitis. Usually a contusion causes swelling within the bursa. The bursa, which had functioned normally up until that point, now begins to develop inflammation, and bursitis results. Once the bursa is inflamed, normal movements and activities can become painful.
Systemic inflammatory conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, may also lead to bursitis. These types of conditions can make patients susceptible to developing bursitis.
As Ronnies is around the elbow it may be Olecranon Bursitis. This could make sense as caused by his traumatic or dramatic fall to the stage in his Victory collapse at the Olympia.
What is olecranon bursitis?
Olecranon bursitis causes fluid to collect in a sac that lies behind the elbow, called the olecranon bursa. A bursa is a slippery, sac-like tissue that normally allows smooth movement around bony prominences, such as the point behind the elbow. When a bursa becomes inflamed for some reason, the sac fills with inflammatory fluid. This can cause pain and a noticeable swelling behind the elbow.
Why did I get olecranon bursitis?
Olecranon bursitis may follow a traumatic accident, such as a fall onto the back of the elbow, or it may seemingly pop up out of nowhere. People who rest their elbows on hard surfaces may aggravate the condition and make the swelling more prominent.
Occasionally, the swelling and inflammation can be the result of an infection within the bursa, this is called infected bursitis.
What is the treatment for olecranon bursitis?
Treatment for routine olecranon bursitis is usually best accomplished by draining the fluid from the sac. Often your doctor will also inject cortisone into the sac after draining the fluid. Cortisone will suppress the inflammatory response to increase the chance of a lasting solution. An oral anti-inflammatory medication is also commonly prescribed.
If there is a question of infection within the bursa, the fluid will be sent for analysis. Treatment of infected bursitis requires repeated drainage of the fluid, antibiotic treatment, and sometimes a surgical procedure to remove the infected bursa. Signs of infection include fevers, chills, redness around the bursa, and suspicious fluid within the bursa. Because of this specific treatment needed, all cases of olecranon bursitis should be evaluated by a physician.
Will olecranon bursitis come back?
Olecranon bursitis can come back, but in a routine case, followed by drainage and resting the elbow, the inflammation usually subsides and the problem resolves. If the bursitis returns persistently, the bursa can be surgically removed, but this is rarely necessary. Often patients will feel a marble-like bump of thickened bursa even months after an episode of olecranon bursitis.
So hopefully all works out fine for Ronnie and it turns out to be this rather than a tricep tear, which would probably be doubtful as he would have experienced severe bruising i.e black and blue arm from shoulder to wrist akin to Dorian Yates or Kevin Levrone when they tore their biceps/triceps.